Main Window
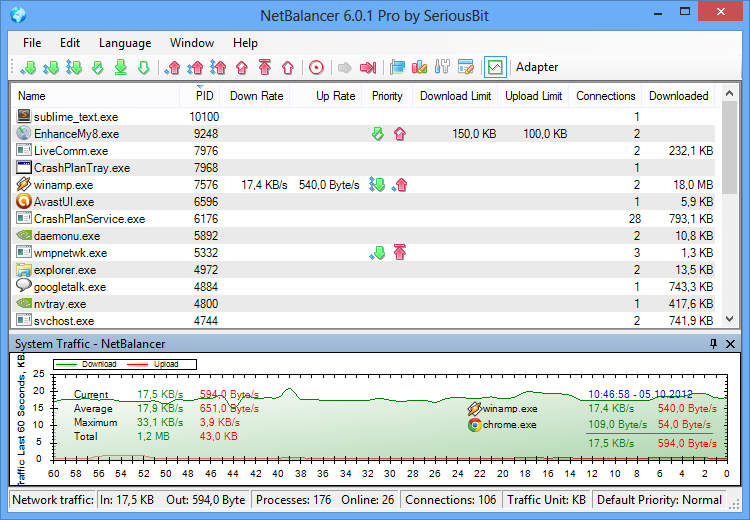
NetBalancer is a software application for monitoring and managing the network traffic of a computer or a group of computers.
It shows you the network traffic on your computer and helps you to set limits, priorities and rules for it.
This is a concept in NetBalancer that is used to delimit the network traffic in 7 main categories:
Also:
Our recommendations is to set for your most important applications a High priority, and for the less important a Low priority. For example set for your streaming application a High priority, so you can watch and listen to the media without any interruptions or hiccups. And set the priority for uTorrent and Download Manager to low, so they wont interfere with your more important applications.
Then, after you are getting used with how NetBalancer works you can set more advanced settings using Limits and Rules.
The Rules are a more advanced method of setting priorities and limits for your traffic. While the basic functionality permits you to set priorities and limits on a per process basis, Rules can be set specifying the network adapter, remote or local IP and Port, network protocol, time and more.
The Filters are just like Rules with the difference that they work at the driver level, and apply to traffic before it enters NetBalancer. A good use for filters is performance optimizations: if there is in your system some critically important traffic that must fly through the wires at the maximum speed possible then set it with filters to be Ignored, so it will go directly to its destination avoiding NetBalancer's limits, priorities and rules, and hence not spending precious milliseconds.
Another useful scenario is blocking at the driver level; although Rules contain the block action too, they lack some Filters only parameters, like MAC address or EtherType protocol.
Yes, rules have the Time panel, where you can select the hours, day of week and/or month and set the appropriate priority for that traffic. You may want to create 2 (or more) rules, for each time period, with different settings.
Yes, add a rule for all your traffic with the traffic limited to, let say 128 kbps, and with the condition "Apply priority only when the traffic of this rule is more than 4GB in the last 1 Month". So when this rule will accumulate 4GB of traffic then all you computer speed will be limited to 128kbps.
Also you can add additional rules, for 4.5GB with a 64kbps limit or even for 5GB with traffic blocked to avoid overpay. Place the 4.5GB rule on top of the 4.GB, and the 5GB rule on top of all of them.
Three methods:
When using grouping you should install NetBalancer on all the computers you want to manage, then for each one go to NetBalancer's menu>Network Adapters>Grouping and add them to the same group (same name). Then set the other settings that are well described in the UI there. Unfortunately, Grouping does not work on all network configurations.
With rules it is easier, but you have to have a gateway computer, i.e. a computer that manages all the Internet traffic for your network. If you already have the gateway then install NetBalancer on it and add the according rules for each managed computer using it's local IP address.
With an external Rules File you don't need a gateway computer, but you should install NetBalancer on all your computers and set them to use the same Rules File. This file can be located on a Windows Share, or it can be a HTTP/HTTPS or FTP link.
At the Traffic Chart, located on the bottom of the NetBalancer's main window. Right click on it to change various settings or copy the viewed data to clipboard and paste it in a text or spreadsheet editor .
It is a tab where are shown all active connection on the current computer. If you select a specific process then the tab will show only that process' connection, if any. Right click on a connection to launch Ping, Trace or other tools on the connection's remote IP.
Run it from the command console as administrator:
NetBalancerSetup.exe /sp- /verysilent /norestart
Right now there are just a few:
/pwd: - sets the password
/priorities_file: - sets the global priorities file
/priorities_file_interval: - sets the global interval at which the priorities file will be re-read
/rules_file: - sets the global rules file
/rules_file_interval: - sets the global interval at which the rules file will be re-read
/serial: - activates NetBalancer during setup
/user_name: - sets the desired user name, that will be shown in About window
When it's done.
NetBalancer keeps its settings in a couple of locations, depending on settings type:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\SeriousBit\NetBalancer are kept the settings of the GUI and Tray apps.HKEY_USERS\Default\Software\SeriousBit\NetBalancer key contains the settings of the NetBalancer's Windows service, except priorities, rules and traffic statistics, which are stored in XML files.C:\ProgramData\SeriousBit\NetBalancer\Rules.xmlC:\ProgramData\SeriousBit\NetBalancer\Priorities*.xml, where * is the ID of the network adapter, a number that can be negative.
Then there are also some files named C:\ProgramData\SeriousBit\NetBalancer\Traffic*.zip that contain various traffic stats.
You can change any of these settings and files, but first you should stop NetBalancer's service, named "NetBalancerService", otherwise it will replace your own settings on shutdown. After you changed the settings start back the service and NetBalancer will load them (it loads them only at start, and then keeps them in memory.)
Report it to us, click in NetBalancer Menu>Help>Report Bug, or please contact us via our Contact page
Ask us, and we'll answer to you directly and eventually add your question here too.